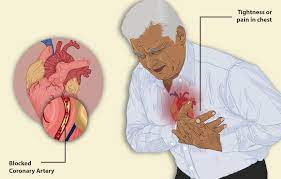
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) refers to a class of disorders that affect the heart or blood vessels, including coronary artery disease (CAD), stroke, and peripheral artery disease (PAD). CVD is the leading cause of death worldwide, with an estimated 17.9 million deaths per year. In this article, we will discuss the causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of CVD.
Causes of Cardiovascular Disease:
CVD is primarily caused by atherosclerosis, a condition in which plaque builds up in the arteries, reducing blood flow and oxygen supply to the heart and other vital organs. Atherosclerosis occurs due to the accumulation of cholesterol and other fatty substances in the walls of the arteries, which can lead to the formation of blood clots or blockages.
Other causes of CVD include hypertension (high blood pressure), which can damage the arteries and increase the risk of heart attack or stroke, and diabetes, which can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of cardiovascular complications. Other factors that can contribute to CVD include smoking, obesity, physical inactivity, and a diet high in saturated and trans fats.
Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease:
Age: The risk of CVD increases with age, particularly after the age of 45 in men and 55 in women.
Gender: Men are at higher risk of CVD than women, although the risk for women increases after menopause.
Family history: A family history of CVD increases the risk of developing the disease.
Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for CVD, as it damages the blood vessels and increases the risk of atherosclerosis.
High blood pressure: Hypertension can damage the arteries and increase the risk of heart attack and stroke.
High cholesterol: High levels of cholesterol in the blood can lead to the formation of plaques in the arteries, increasing the risk of CVD.
Diabetes: Diabetes can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Obesity: Obesity increases the risk of CVD, as it can lead to hypertension, high cholesterol, and insulin resistance.
Symptoms of Cardiovascular Disease:
The symptoms of CVD can vary depending on the type of disorder and the severity of the condition. Some common symptoms of CVD include:
Chest pain or discomfort: This is a common symptom of CAD and may occur during physical activity or emotional stress.
Shortness of breath: This may occur during physical activity or at rest and may be a sign of heart failure or pulmonary edema.
Fatigue: This may be a sign of heart failure or other cardiovascular disorders.
Swelling in the legs or ankles: This may be a sign of heart failure or peripheral artery disease.
Dizziness or lightheadedness: This may be a sign of low blood pressure or arrhythmia.
Rapid or irregular heartbeat: This may be a sign of arrhythmia or other cardiovascular disorders.
Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease:
The diagnosis of CVD may involve several tests and procedures, including:
Physical exam: This may include checking the patient's blood pressure, heart rate, and other vital signs.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test measures the electrical activity of the heart and can detect abnormalities in heart rhythm or structure.
Echocardiogram: This test uses sound waves to create images of the heart and can detect abnormalities in heart structure or function.
Stress test: This test involves monitoring the patient's heart rate and blood pressure while they exercise to evaluate the heart's response to physical activity.
Cardiac catheterization: This procedure involves inserting